Complex metropolitan regions, with several urban centers, are more economically efficient and less dependent on energy consumption
New LET study about how to measure large-scale complex urban network structures using night-time light satellite databases applied to European metropolitan regions.
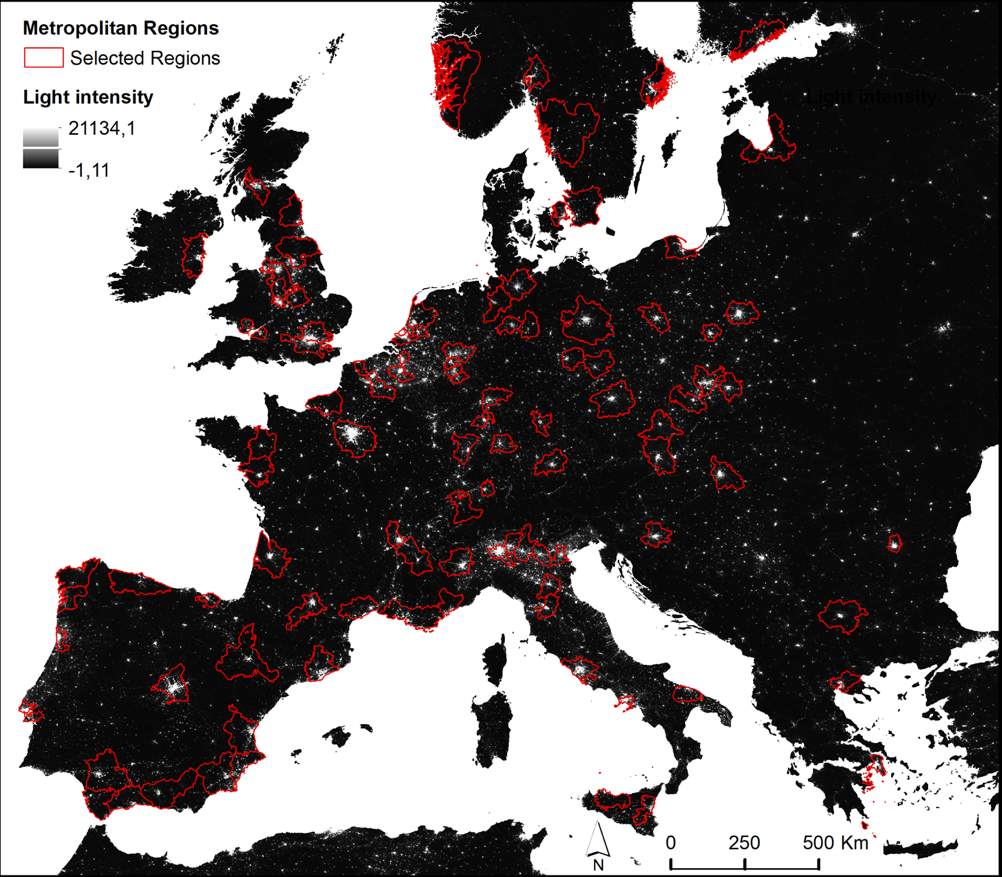
This study has evaluated the urban network structure of 100 European metropolitan regions using satellite data on night lighting, concluding that polycentric urban networks create more innovation, which allows them to be more economically efficient and less dependent on energy consumption.
The aim of the study is to develop indicators to test the hypothesis that complex urban networks are more efficient economically and less dependent on energy consumption owing to better information organization. It uses NPP-VIIRS NTL satellite data on night lighting (NTL) and employs a topographical representation of NTL intensities to detect urban centers. Based on the distribution of NTL intensities in urban centers represented as a Lorenz curve, it develops two new indicators of monocentricity and polycentricity to evaluate large-scale urban network structures.
Further research should study in greater detail the relationships between urban network structures and their social, economic, and ecological performances.
Consult the paper.